The growth and popularity of bitcoin (BTC) has reached such heights over the last decade that it has given birth to a whole mining industry.
Thousands of individuals and companies compete to produce the next Bitcoin block in return for block rewards.
The industry has become so competitive that individuals must consider whether bitcoin mining at home is worth the high energy and hardware expenses.
Is mining bitcoin profitable? Let’s find out.
Understanding Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is a fundamental part of the Bitcoin protocol. It is the process that keeps the network ticking.
Not only do bitcoin miners process transactions, but they also prevent fraudulent activities and double-spending of coins. The Bitcoin protocol can not function with its miners.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of proposing and creating new blocks on the Bitcoin blockchain, for which miners are rewarded with newly minted BTC. The primary function of bitcoin mining is to prevent bad actors from defrauding the network and its participants.
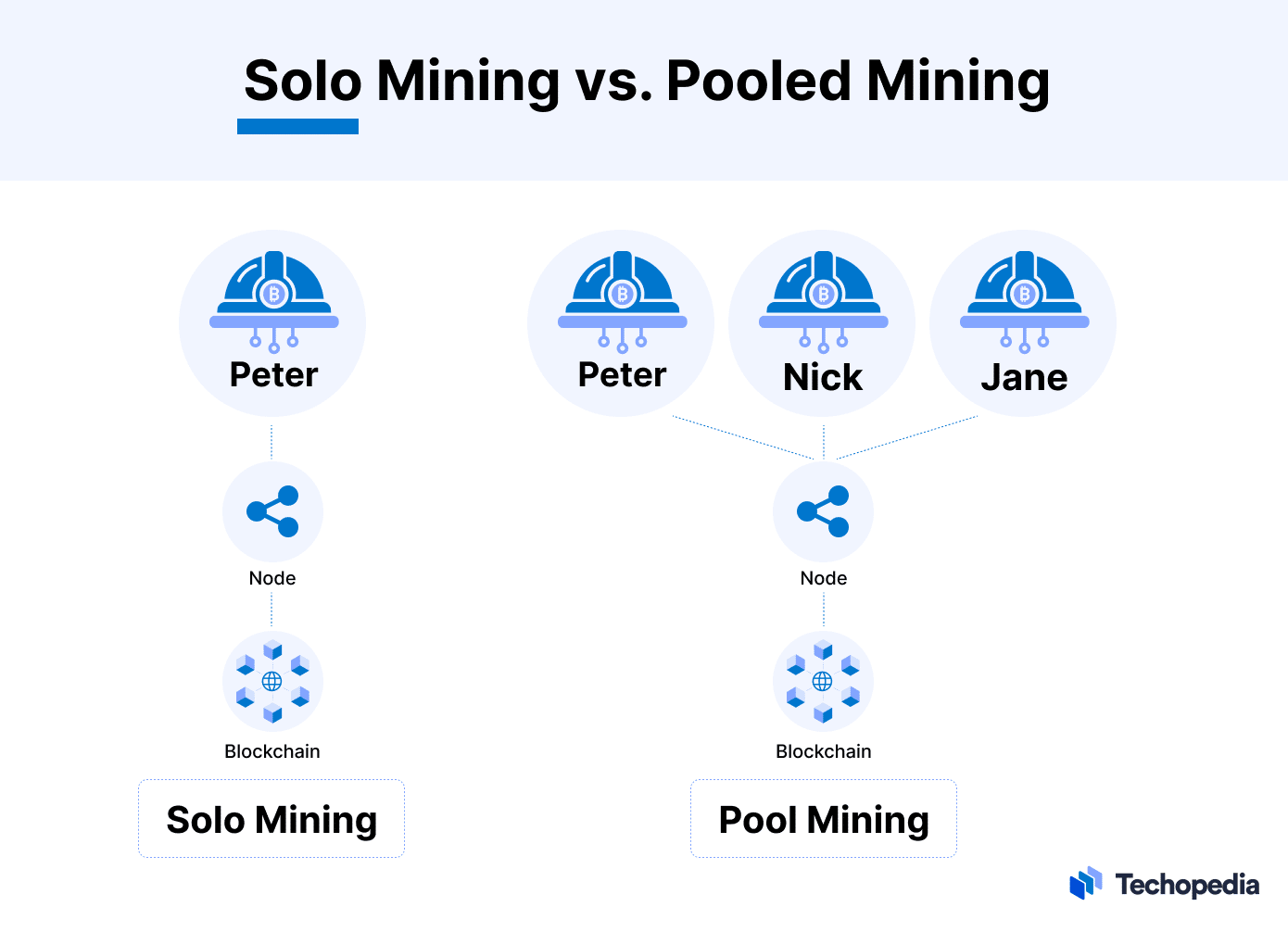
Bitcoin mining comes in two forms: solo mining and pooled mining.
- Solo mining refers to a single entity (individual or company) attempting to generate new blocks on their own and keeping block rewards for themself, e.g., by mining bitcoins at home.
- Pooled mining refers to several miners (individuals or companies) coming together to produce blocks more frequently. The pool members share the proceeds according to the hashing power contributed.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
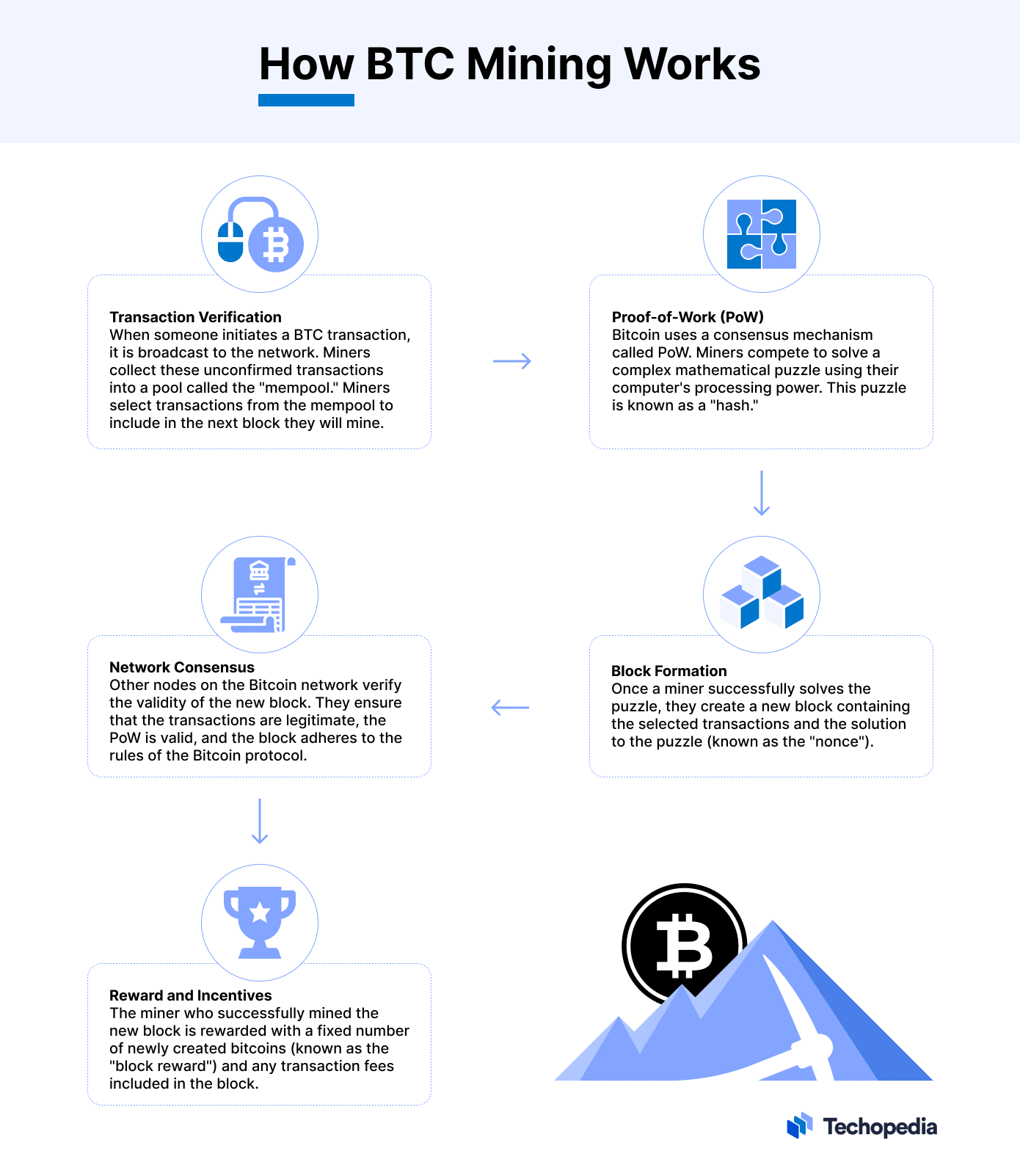
Bitcoin miners protect the network by solving cryptographic puzzles that prove the validity of the transactions in the block.
The first miner to solve the puzzle wins the chance to propose and create the next block of the Bitcoin blockchain.
If all the other miners and nodes come to a consensus regarding the proposed block’s validity, a new block is added to the blockchain. The miner receives newly-minted BTC in return for their effort.
Creating the block is not the only way bitcoin miners earn BTC. Miners also receive gas fees for processing transactions.
How to Mine Bitcoin at Home?
Gone are times when you could run a profitable mining operation from your laptop. The bitcoin mining industry has become hyper-competitive, mainly resulting from technological advancements in mining hardware.
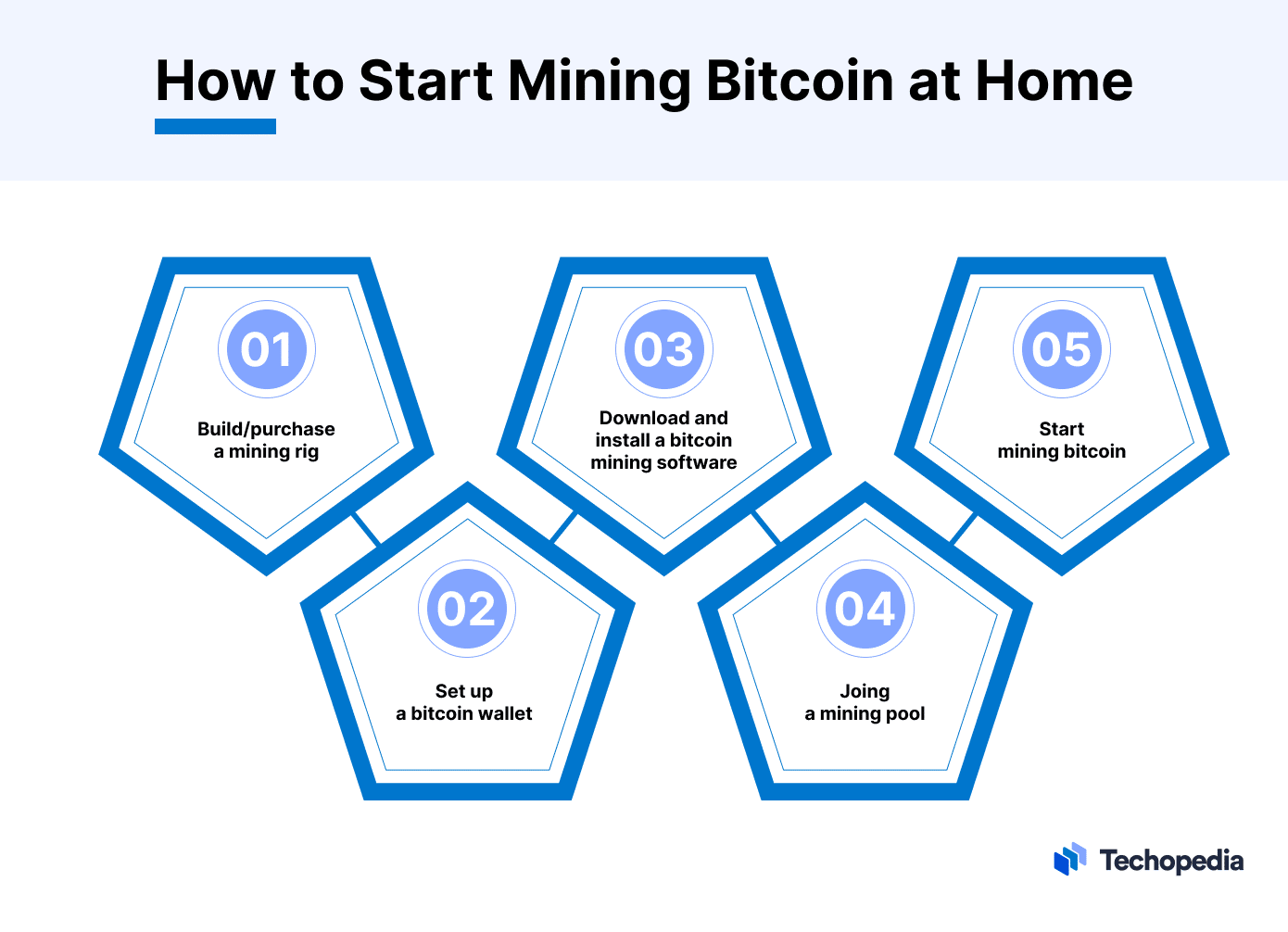
Here is what you need to mine bitcoin at home (competitively):
- Mining rigs
A mining rig is a computer custom-built to mine cryptocurrencies. A rig consists of multiple components and chips. Different types of mining rigs are categorized according to the type of chips they use.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The chip that powers your laptop. Although it is technically possible to attempt mining bitcoins with your PC, CPU chips are not optimized to serve as bitcoin mining gear. Mining bitcoins with your PC may not be profitable.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Units)
A GPU mining rig is the upgrade to the CPU rig. It can be a regular computer that is loaded with several GPU chips.
Although GPU rigs increased mining efficiency significantly compared to CPU rigs, they are not explicitly created for crypto mining. GPU chips are designed for gaming and video rendering.
- FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array)
FPGAs are integrated circuits that are best known for their programmability. Users can reconfigure the hardware to mine a specific coin based on the cryptocurrency’s network’s cryptographic hash algorithm.
- ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit)
ASIC mining rigs are the top-performing bitcoin mining hardware in the market today. These rigs are customized and built only to mine cryptocurrencies. Therefore, they outperform other chips in performance and energy efficiency.
- Software
Today, most ASIC mining rigs come with pre-installed mining software. If a miner wants to use different mining software, they can download them online. Some examples of bitcoin miner software are ASICSeer, CGMiner, and MultiMiner.
A few other resources are required:
- Energy source
- Internet connection
- Cooling infrastructure
- A computer to monitor operations, join mining pools, analyze the market
Setting Up Your Mining Operation
After selecting the proper mining hardware and software that suits your needs, expectations, and expenses, you will need to set up your mining rig correctly.
- Placement: The bitcoin mining rig needs to be placed in a spacious room to be accessible when repairs are needed.
- Cable and electricity management: You will need to ensure that your mining rig is connected to a reliable source of electricity. You may need to set up a backup power source to keep operations running. It is also important to use good-quality cables, wiring, and circuit breakers to protect your hardware.
- Internet: Professional miners prefer using ethernet and LAN cables when connecting their rigs to the Internet as they are more reliable than WiFi connections.
- Connecting a wallet: If you want to start mining BTC at home, you will need a crypto wallet where bitcoin rewards can be sent.
Joining a Mining Pool
Joining a mining pool is considered a reliable way to mine bitcoin at home. A mining pool can result in a steady bitcoin payout from mining operations.
Bitcoin Mining Pools Explained
A mining pool groups together mining resources and distributes block and transaction rewards to contributing miners based on their share of work.
There are numerous mining pool options available to miners. Notable names include F2Pool, AntPool, and Binance Pool. A miner will need to apply to join a mining pool.
The mining pools will differ according to their hashrate, fee structure, and payout structure. A mining pool may even allow miners to mine different types of cryptocurrencies.
User payout typically depends on the hashrate provided by the miner. Profit from operations will differ from one miner to another based on their hardware expenses and operational costs.
Other factors, such as bitcoin prices, pool fees, mining difficulty, and payout schemes, will also affect miner profits.
Users have to be aware of the threats of hacks and thefts when using cryptocurrencies. How can bitcoin miners protect themselves?
Protecting your Mining Operation from Cyber Threats
Bitcoin miners need to be aware of viruses and malware tactics that can hijack crypto-mining hardware.
There is a term called cryptojacking, which refers to mining cryptocurrencies using computing resources from infected hardware. A victim of cryptojacking may not even notice that their system has been compromised.
CPU and GPU mining rigs are especially vulnerable to cryptojacking. Viruses and malware can enter your mobile device and computers by downloading files and mobile apps. Users can protect themselves by steering clear of suspicious links, using antivirus and VPN software, and avoiding public WiFi networks.
Best Practices for Securing Your Bitcoin Wallet
Your crypto wallet is where you will hold your bitcoin mining rewards. Your wallet needs to be protected. Here are some tips to secure your crypto wallet:
Secure your private keys: The private key is the password to your wallet. Storing your private keys offline (by writing them on paper) is one way to safeguard them from hacks.
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket: Spreading your crypto holding across several wallets will ensure you don’t lose everything in case you get hacked.
Using a cold wallet: Cold wallets are considered the safest way to protect your cryptocurrencies as they are not connected to the internet.
Multi-signature wallet: Multi-signature feature ensures that your bitcoin can only be spent/transferred after multiple approvals.
Plus, you should always avoid suspicious websites and links and not publish sensitive information online.
What You Need to Know Before Mining Bitcoin at Home
Monitoring and analyzing the bitcoin mining industry and bitcoin prices can be crucial to turning a profit. Here are some technical details you need to know before you start mining bitcoin.
- Mining difficulty
Bitcoin has a self-regulating property called difficulty adjustment. Difficulty adjustment refers to the change in the mining difficulty so that the time between two adjacent bitcoin blocks is always 10 minutes.
Simply put, increasing online miners will make the cryptographic puzzle more challenging. Fewer online miners mean easier cryptographic puzzles. Mining difficulty is adjusted once every 2016 blocks, which is approximately 14 days.
- Hashrate
But how will you know how many miners are currently online? There are so many of them in the world. Your answer is hashrate.
Hashrate is a vital mining metric that measures the Bitcoin network’s computation power.
Higher hash rates indicated that more miners are online. Network hashrate data is available online.
- Halving
Miners receive block rewards for creating new blocks. These block rewards are not constant. They are designed to decrease over time.
Halving is an event that occurs after the Bitcoin network mines 210,000 blocks, which can take roughly four years.
Halving results in bitcoin block rewards being cut in half.
The most recent halving event occurred in May 2020 when block rewards were reduced to 6.25 BTC per block from 12 BTC per block.
Block rewards are designed to ultimately reach zero, which is expected to occur in 2140. After this, bitcoin miners will have to rely solely on transaction fees as their source of income.
- Market cycle
Miner profitability is directly linked to BTC prices. Therefore, bitcoin miners must strategize their operations, expense, and expansion plans according to market cycles. Market cycles not only affect miner profitability but also affect technical aspects like mining difficulty.
For example, high BTC prices will lead to higher miner profits. Higher profits will encourage miners to invest in more and newer mining rigs. This will result in a higher network hashrate and make mining more difficult.
Lower BTC prices may force unprofitable miners to shut down their mining operations, resulting in lower mining difficulty.
Some miners may even see a bearish market as an opportune time to buy mining rigs for cheaper prices, which will help them gain market share.
Risks Involved in Bitcoin Mining
- Investment risk
Today, the competition has made CPU and GPU rigs obsolete. To mine bitcoin competitively from home, you will need ASIC rigs.
But ASIC rigs are expensive.
The cheapest bitcoin-specific mining gear on rig maker Bitmain’s website was priced over $4,600 at the time of writing. The top model Bitcoin Miner S19 XP Hyd was about $8,500. Even with this high-end mining rig, your mining operation is not guaranteed to be profitable.
- Operating expenses
Mining bitcoin is not free. The process is highly energy-intensive, meaning high electricity fees. Regular maintenance and internet expenses are other overheads that miners need to consider.
- Competition
The mining industry is highly competitive. You will be up against professional and well-funded bitcoin mining companies. Other factors like hashrate and mining difficulty will also come into play.
- Hacks
Hacks and thefts of cryptocurrencies are everpresent threats in the crypto sector. Bitcoin miners will have to stay alert or risk losing their earnings.
- Environmental risk
Bitcoin mining is not considered environmentally friendly, with mining rigs needing to be constantly connected to a power source to be competitive.
- Legal risk
Cryptocurrencies and crypto mining activities are not legal in some countries.
The Bottom Line
The bitcoin mining industry is a fast-evolving one. It was easy to mine bitcoin from your home in the early days using a laptop.
Today, the technological advancements in mining rigs and the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies have made it almost impossible to mine bitcoin using simple devices.
However, mining still has plenty of opportunity for those with scale and opportunity to jump in.
FAQs
How much does it cost to mine bitcoin?
How long does it take to mine one bitcoin?
How does bitcoin mining work?
Is bitcoin mining legal?